Importance Of Integrated Pest and Disease Management (IPDM)
Integrated Pest and Disease Management (IPDM) in Vegetable Production
Integrated Pest and Disease Management (IPDM) is a sustainable approach that combines various strategies to manage pests and diseases in vegetable production. This method is important in today’s climate crisis, as it helps maintain ecosystem balance, reduces chemical reliance, and enhances resilience to climate-related challenges. Let's look at some of these management practices and how they can contribute to eco-friendly production in daily vegetable farming.
1. Cultural Practices
Crop Rotation: Rotating different crops disrupts pest and disease cycles. For instance, alternating leafy greens with legumes can reduce vulnerability to soil-borne pathogens, enhancing soil health and biodiversity.
Intercropping: Growing diverse crops together, such as tomatoes with marigolds, can confuse pests and lower infestations. This diversity not only promotes pest control but also improves soil quality.
2. Biological Control
Beneficial Insects: Introducing natural predators like ladybugs can effectively manage pest populations. These insects contribute to a balanced ecosystem, reducing the need for chemical pesticides.
Microbial Agents: Utilizing beneficial microbes, such as Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt), provides a targeted approach to pest control without harming beneficial organisms or pollinators.
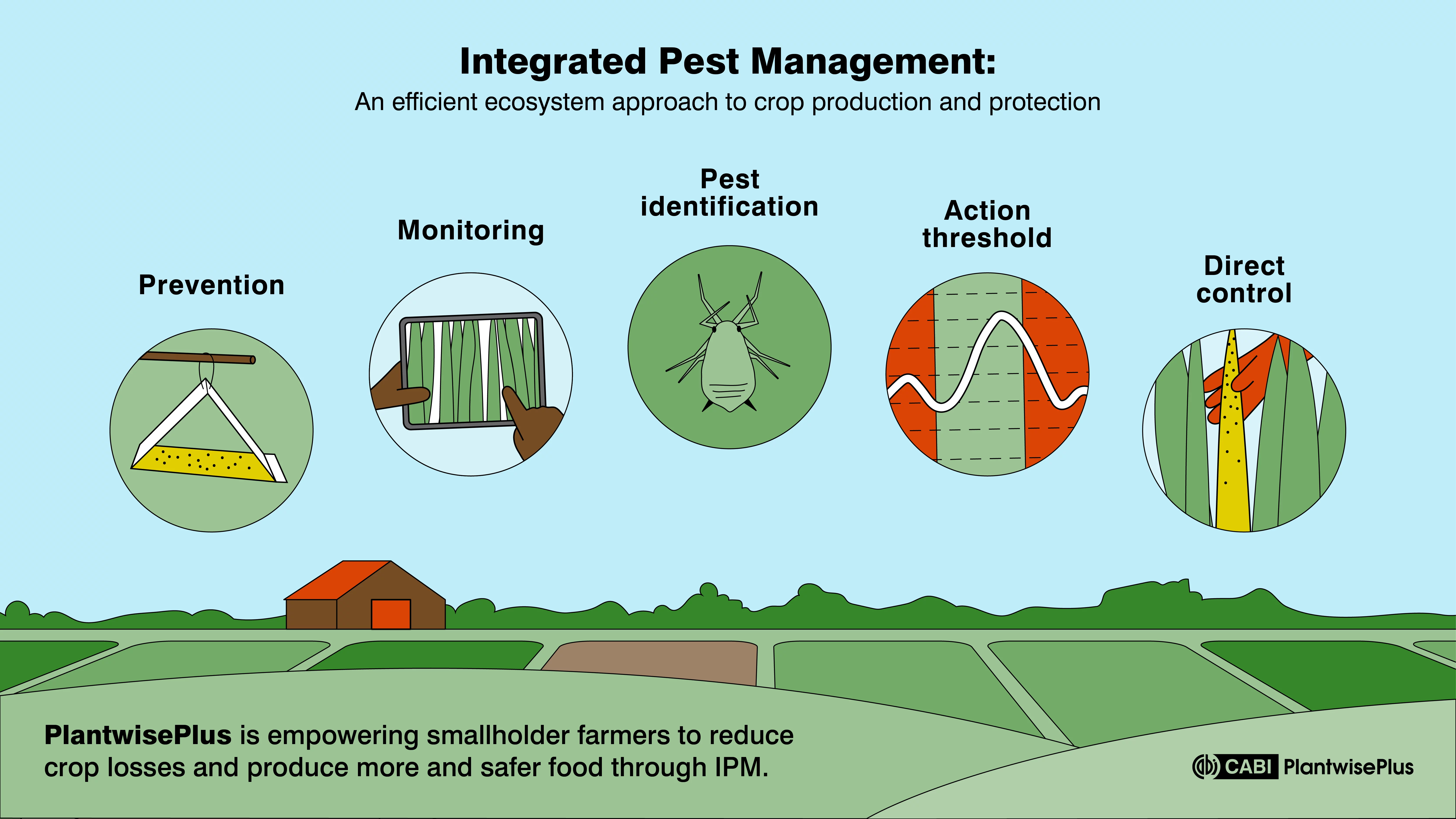
3. Monitoring and Thresholds
Regular Monitoring: Conducting frequent inspections helps identify pest outbreaks early. Tools like traps and visual assessments enable timely interventions, minimizing crop damage.
Action Thresholds: Establishing economic thresholds informs farmers when pest populations warrant control measures, preventing unnecessary pesticide use and promoting cost-effectiveness.
4. Chemical Controls
Targeted Pesticide Use: When chemical intervention is necessary, applying pesticides strategically based on monitoring data minimizes environmental impact. Choosing eco-friendly options can further reduce harm to non-target species.
Integrated Application: Combining biological methods with selective pesticides enhances overall effectiveness while lowering chemical dependence.
5. Education and Community Engagement
It is very important for farmers to adapt to some of these integrated pest and disease management (IPDM) practices to ensure produce is of less or no chemicals, and also this can help protect our environment, ensuring sustainability. These practices also help ensure that consumers consuming produce that is sustainably grown using some of these techniques are free from any future health complications, and more importantly, they also ensure food safety and integrity within the food system.
Importance in the Climate Crisis
As climate change alters weather patterns, pests and diseases become more unpredictable. IPDM enhances agricultural resilience by promoting biodiversity and ecosystem health, which are vital for adapting to these changes. By reducing chemical inputs and improving soil health, IPDM not only sustains vegetable production but also mitigates environmental degradation.
Conclusion
Implementing IPDM in vegetable production is essential for sustainable agriculture, especially in the face of climate challenges. By integrating various management strategies, farmers can effectively combat pests and diseases while fostering resilience and sustainability in their practices.
Feel free to give us a comment, especially if you need more explanation on some of the practices, such as how the action threshold works and how it is done
